PDF chapter test TRY NOW
In the twentieth century, it was discovered that atoms of all elements are made up of smaller components such as electrons, protons and neutrons. An electron from a hydrogen atom has no difference from the electron of a carbon atom. Likewise, protons and neutrons of all elements also have identical characteristics. These particles that build the atom are called Subatomic particles.
Subatomic particles of an atom
Proton, electron and neutron
Proton:
Ernest Rutherford discovered positively charged particles called protons. The positive charge of a proton is of the same magnitude as that of the electron's negative charge. It is denoted by the letter '\(p\)'.
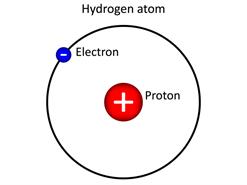
Hydrogen atom
Neutron:
James Chadwick, a scientist, discovered a neutron. Neutron is located inside the nucleus. It does not have any charge, and it is electrically neutral. Other than hydrogen, the nuclei of all the atoms contain neutrons. A hydrogen atom has no neutron because its nucleus is the smallest in size, which cannot accommodate any heavier neutron. Neutron is denoted by the letter '\(n\)'.
Electron:
Electrons are negatively charged particles discovered by J J Thomson. They revolve around the nucleus of the atom in fixed orbits. Mass of the electron is negligible when compared to the mass of a neutron or proton. Hence, the mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
The nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons. They are commonly called nucleons. The total negative charge of all electrons outside the nucleus is equal to the total positive charge in the nucleus. Thus, it makes an atom to be electrically neutral. Electron is denoted by the letter '\(e\)'.

Electrons revolves around the nucleus
