
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoThe filament in bulbs:
Important!
Thomas Alva Edison invented electric bulb. He has invented around \(1300\) products, including the gramophone, the motion picture camera and the carbon transmitter.
Generally, when the current passes through a conductor, some elements easily get heated up and emit light.
A filament is a small wire used in electric bulbs. Usually, the filament is made of a material with a high melting point.

Filament in bulb
Tungsten is commonly used as a filament in electric bulbs. This filament is thermally isolated by placing between two thick connecting wires in an electric bulb. Some properties of tungsten are listed below.
- It has high resistivity.
- It has a high melting point (\(3380\ °C\)).
- It is not easily oxidised.
When a large amount of current is passed through the wire, the filament reaches a high temperature and starts glowing.
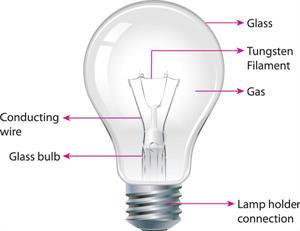
Parts of a light bulb
Since the filament attains a higher temperature, it starts evaporating and decreases the efficiency of the bulb. The bulb is filled with inactive nitrogen and argon gases at low pressure to avoid evaporation of the filament. The gas, in turn, helps to maintain the filament at high temperatures and prolongs the life.
A bulb becomes fused if there is a break in the filament of an electric bulb. Due to the break in the path of the current, the fused bulb does not glow.
Electric fuse wire:
An electric fuse is a safety device that prevents electric fires or damages to electrical appliances due to excessive current flow.

Electric fuse
The fuse consists of a ceramic or porcelain body and two points for connecting the fuse wire. The fuse wire is made of a metal or an alloy containing \(50 \%\) lead and \(50 \%\) tin. The fuse wire can also be made with materials like aluminium, copper, iron, etc. Some properties of fuse wire are listed below.
- It has a high resistivity.
- It has a low melting point.
Due to high resistance, some materials in the wires melt quickly and break when a large amount of current is passed through them. Electric fuse wire connected in series in electrical circuits uses a material with a low melting point.
There is a safety limit for the current to flow in the circuit. The wire gets overheated and melts if the current exceeds this limit due to Joule’s heating effect.
In this scenario, the fuse will blow off when the circuit is broken. The safety device, fuse prevents the circuits from any damages occurring due to fire.
For domestic purposes, the fuses at a rate of \(1\ A\), \(2\ A\), \(3\ A\), \(5\ A\), \(10\ A\), etc,. are usually used. For example, if an electric iron consumes \(1\ kW\) electric power when operated at \(220\ V\). Then, the rate of current required for the fuse can be calculated using the formula,
On substituting the above values, we get
The current of \(4.54\ A\) flows in the circuit, and hence a fuse of \(5\ A\) must be used.