
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoThe process of development of a new plant from the seed is known as germination.
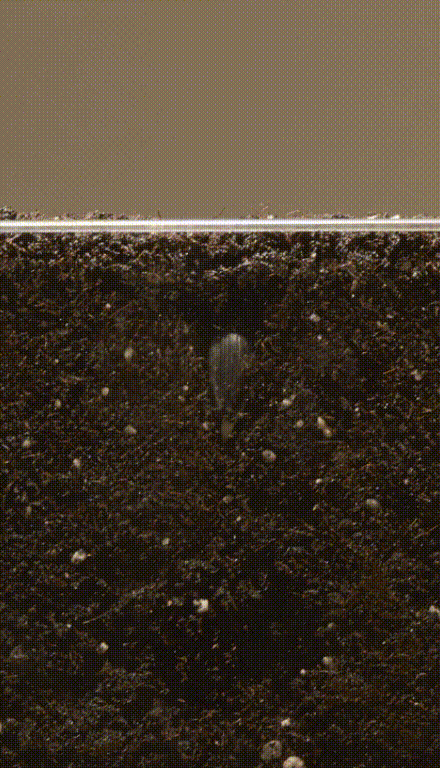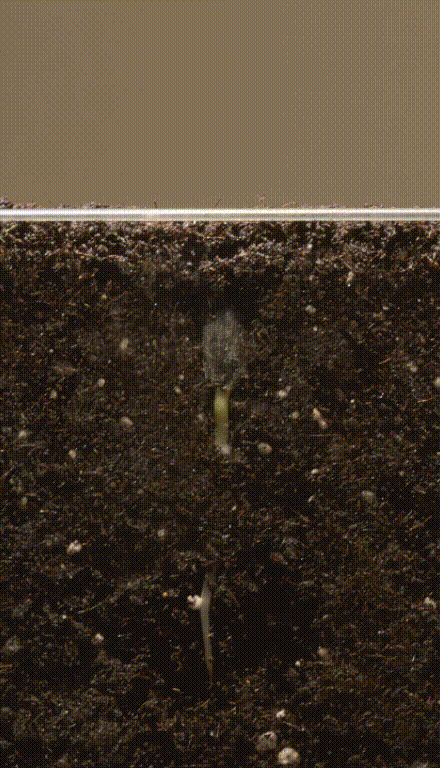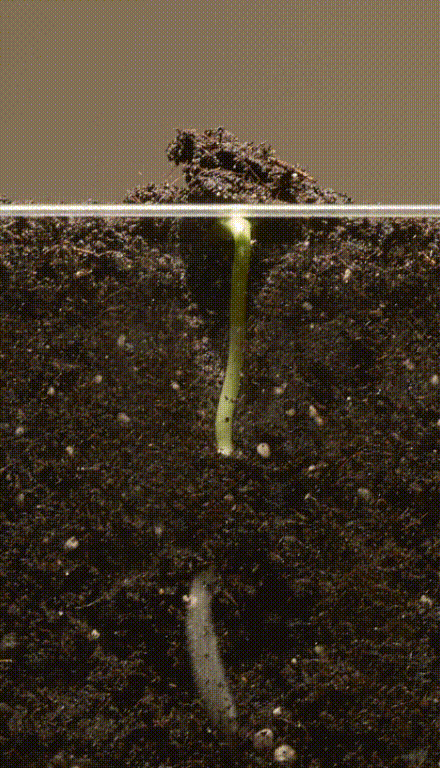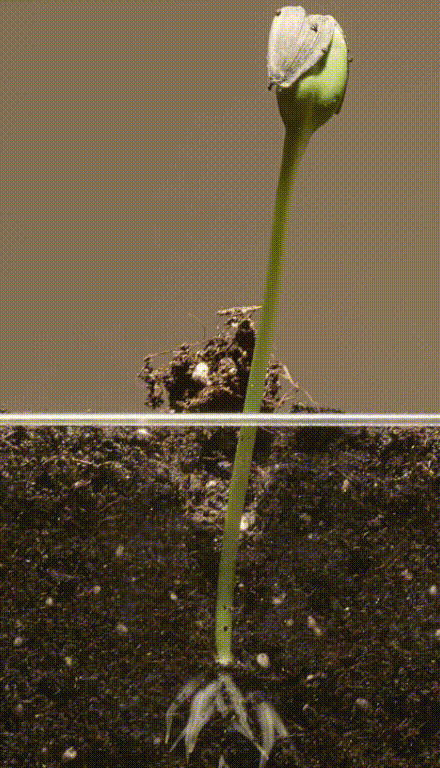
Germination of seed
It is a slow biological process. Hence, the seeds in a dry state are alive, but remain dormant.
Conditions necessary for germination:
- Water
- Air (oxygen)
- Favourable temperature
- It helps in softening by of the seed by rupturing the seed coat.
- Allows the plumule and radicle to emerge out of the seed coat.
- Converts the stored food into soluble material.
- Transports the soluble food from the storage tissue to the embryo.
Role of oxygen in seed germination:
- It provides energy required for the process of germination.
- It facilitates aerobic respiration to liberate energy.
- Increases the rate of respiration.
- Oxidation of food takes place with the help of oxygen.
- As different biological processes takes place during the process of respiration an optimum temperature is required.
- Hence, maintenance of an optimum temperature ranging from \(25\ to\ 35°C\) is required,
Types of germination:
Germination of seeds occurs in two ways:
- Hypogeal
- Epigeal
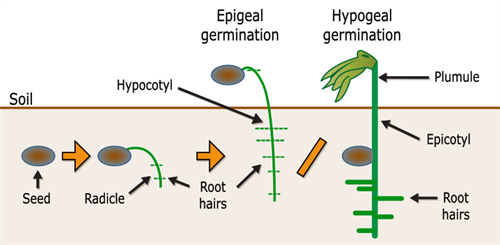
Different types of germination
Hypogeal germination in seed:
In the term hypogeal 'hypo' refers to below and 'geo' refers to earth.
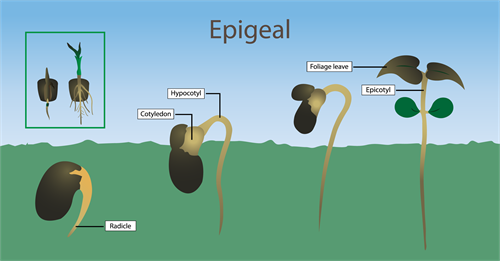
Epigeal germination
- During this type of germination the seeds swell due to the absorption of water leading to the bursting of testa.
- The radicle emerges and grows downwards and forms the root.
- The plumule grows upwards and forms the shoot.
In the term epigeal 'epi' refers to above and 'geo' means earth.
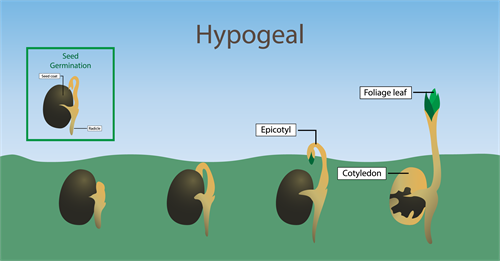
Hypogeal germination
- During this type of germination the seeds swell due to the absorption of water.
- The radicle emerges and grows downwards and forms the root.
- Hypocotyl forms an arch and grows above the soil, and brings the cotyledons above the soil.
Reference:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c7/Sunflower_growing_time_lapse.gifhttps://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Germination-en.svg