
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoA simple electric circuit
An electric circuit is a continuous closed path along which current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery.
Construction of a circuit
An electric circuit consists of a cell, connecting wires, a bulb, and a switch.
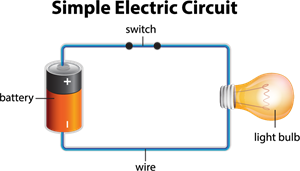
A cell or a battery is the main source of electric current.
A cell is a single unit, whereas a battery is a collection of cells.
The connecting wires are used for carrying current across the circuit, and a bulb (or a lamp) is a small device that consumes the electricity.
An electric switch or a key is connected to the circuit to stop or allow the flow of current.
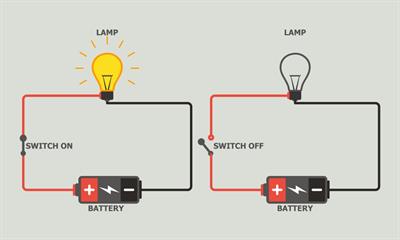
If a key is in open condition (switched off state), the current will not flow across the circuit; thus, it is an open circuit. A bulb does not glow in this type.
If the key is closed (switched on), then the current will flow, making it a closed circuit. A bulb glows in this type.
If the key is closed (switched on), then the current will flow, making it a closed circuit. A bulb glows in this type.
The two terminals of the electric cell connected to the bulb can form a simple electric circuit. This provides a complete path for current to flow between the two terminals of the electric cell.
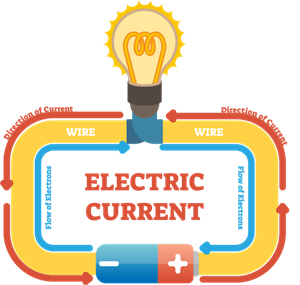
The direction of the current is always from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery.

In this arrangement, one end of a wire is connected to the base of a bulb, and the other end is given to the negative terminal of a cell. When the tip of the base of the bulb is in contact with the positive terminal of the cell, the bulb glows.

When the bulb is taken away from the terminal of the electric cell, the bulb does not glow. A bulb becomes fused if there is a break in the filament. Due to the break in the path of the current, the fused bulb does not glow.