
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoIntroduction:
- We can see the objects around us through our eyes. However, we cannot see anything around us without light or in darkness.
- When light falls on the object, our eyes detect that light, and hence the object becomes visible to us. Thus light makes things visible.

Candle - Light source
Depending on the interaction of light with materials, the objects can be classified into three types.
- Opaque
- Transparent
- Translucent
Click on this link to know more about opaque, transparent, and translucent objects.
What happens when light falls on a mirror?
- Light is a form of energy which is responsible for the sense of sight in the human eyes.
- Sometimes, light can be called radiation that is emitted, reflected, or absorbed by different objects.
Mirror:
A mirror is a material made up of glass having a shiny surface. When light falls on a mirror, it is reflected back. So, a mirror changes the direction of light that falls upon it.
Reflection:
The bouncing back of light from a smooth surface is called reflection. Smooth polished surfaces called mirrors can reflect light falling on them in any direction.
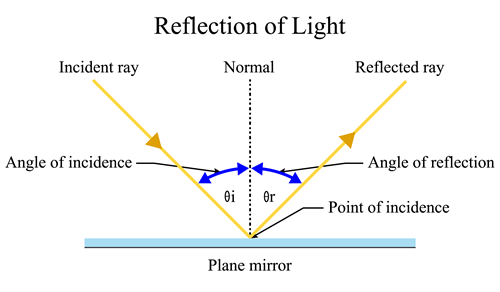
Reflection of light
Know the terms,
Incident ray: The light ray that falls on the surface is called the incident ray.
Reflected ray: The light ray that gets reflected from the surface is called the reflected ray.
Normal: It is an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point where the incident ray strikes the surface or at the point of incidence.
The angle of incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
The angle of reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle of reflection.
Laws of reflection:
The first law of reflection:
The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
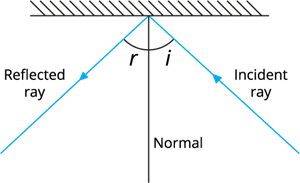
Incident and reflected ray
The second law of reflection:
According to the second law of reflection, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection. (\(<i\) \(=\) \(<r\))
Reference:
https://pixabay.com/photos/hands-open-candle-candlelight-1926414/