
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoSeries connection of parallel resistors:
A series-parallel circuit is formed by connecting a set of parallel resistors in series.
- Connect \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) in parallel to obtain an effective resistance of \(R_{P1}\).
- Similarly, connect \(R_3\) and \(R_4\) in parallel to get an effective resistance of \(R_{P2}\).
- These parallel segments of resistors are then joined in series.
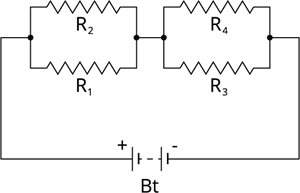
Series-parallel combination of resistors
The formula for the effective resistance of the parallel combination of resistors is
For two resistors in the circuit, the effective resistance is given as
Using the effective resistance of the series circuit, , the net effective resistance of the series-parallel combination of resistors is,
Parallel connection of series resistors:
A parallel-series circuit is formed by connecting a set of series resistors in parallel.
- Connect \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) in series to get an effective resistance of \(R_{S1}\).
- Similarly, connect \(R_3\) and \(R_4\) in series to get an effective resistance of \(R_{S2}\).
- These series segments of resistors are then joined in parallel.
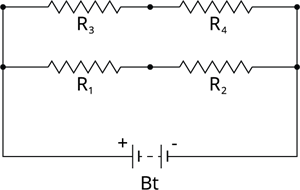
Parallel-series combination of resistors
Using the effective resistance of the series circuit, , we get
Using the formula for the effective resistance of the parallel combination of resistors , the net effective resistance of parallel-series combination of resistors is
.