PDF chapter test TRY NOW
3. Shale gas:
Shale is a soft, finely stratified sedimentary rock formed from the compaction of small ancient rocks containing mud and minerals such as quartz and calcite trapped beneath the earth's surface. In the pores of these rocks, fossil fuels such as oil and gas can be found.
Fossil fuels can be extracted through hydraulic fracturing (drilling or well boring of sedimentary rock layers to reach productive reservoir layers).
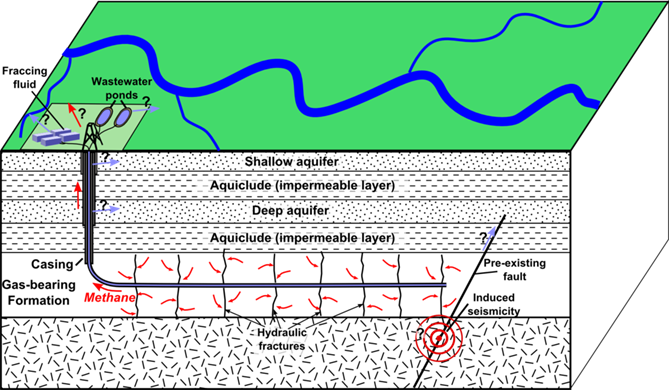
Shale gas extraction
Environmental concerns of using shale gas:
1. Shale drilling may impact on groundwater reserves, contaminating drinking water supplies and reducing soil fertility.
2. Millions of gallons of water are required to break and release shale gas, affecting the water table.
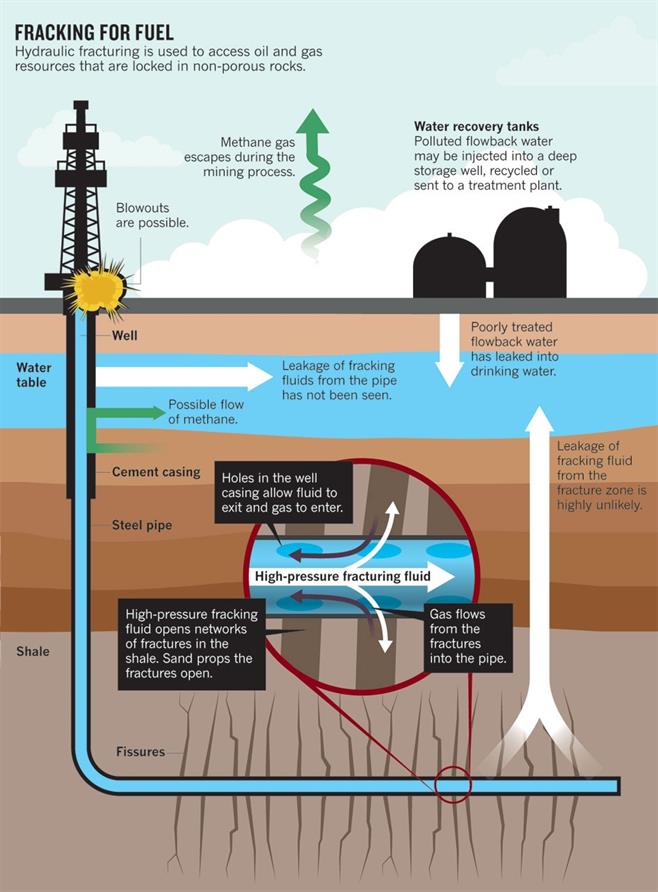
Image credits: Environmental impacts of shale gas
Important!
The Cambay (Gujarat), Assam-Arakan (North East), Gondwana (Central India), Krishna Godavari onshore (East Coast), Cauvery onshore, and Indo- Gangetic basins have all been considered as potential shale gas exploration regions in India.
Reference:
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HydroFrac.png
https://www.nature.com/articles/477271a
