
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free Demo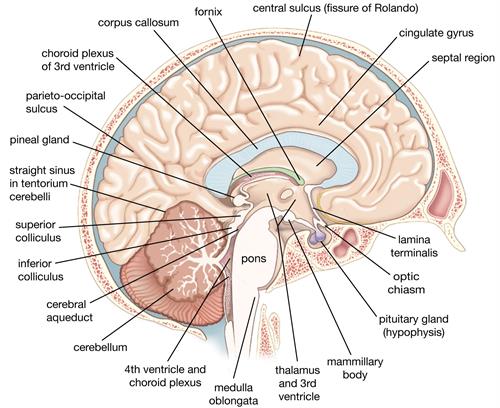
- Corpora quadrigemina has two parts: (i) Superior colliculi - controls visual reflexes (ii) Inferior colliculi - controls auditory (hearing) reflexes
- Crura cerebri relay impulses back and forth between the cerebrum, cerebellum, pons and medulla.
- Two large-sized hemispheres
- Middle vermis
- Respiratory control centre - controls respiration
- Cardiac centre - controls heartbeat
- Vasomotor centre - controls contractions of blood vessels
- Diencephalon
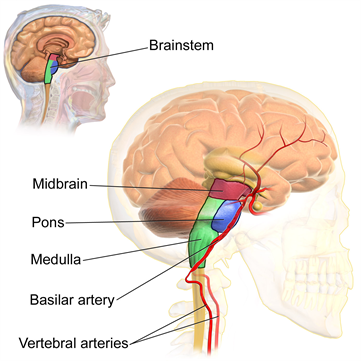
- Medulla oblongata
- Pons Varolii
- Midbrain
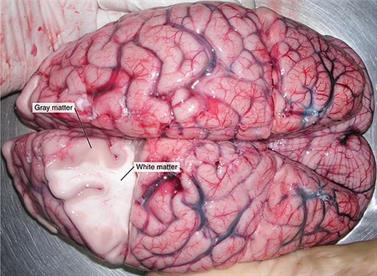
- The cell bodies and dendrites of neurons, as well as supporting cells called astroglia and oligodendrocytes, make up grey matter.
- White matter, on the other hand, is largely made up of axons that are wrapped in myelin.
- Grey matter neurons do not have long axons, unlike white matter neurons.
- Grey matter accounts for \(40\%\) of the brain's volume, whereas white matter accounts for \(60\%\).
- Grey matter gets its colour from the grey nuclei that constitute the cells. The white appearance of the white matter is due to myelin.
- Grey matter completes processing, whereas white matter facilitates communication between grey matter regions and between grey matter and other parts of the body.
- Grey matter does not have a myelin coating, but white matter possesses it.
Structure | Functions |
| Cerebral cortex | Sensory perceptions, control of voluntary functions, language, thinking, memory, decision making, creativity |
| Thalamus | Acts as a relay station |
| Hypothalamus | Temperature control, thirst, hunger, urination, an important link between nervous system and endocrine glands |
| Cerebellum | Maintenance of posture and balance, coordinate voluntary muscle activity |
| Pons and medulla | Role in sleep-wake cycle, cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive control centres. |
Nearly \(60\%\) of the human brain is made up of fat. Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are crucial substances that determine the integrity and ability of our brain.
Food is the only way to get EFAs because our bodies cannot synthesise them. EFAs are abundant in fish, green leafy vegetables, almonds and walnuts.
The electroencephalogram (Gbe) is a device that records electrical impulses in the brain. EEGs can detect abnormalities in brain waves and aid in diagnosing seizures, epilepsy, brain tumours and head injuries, among other conditions.
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/83/Diagram_showing_the_brain_stem_which_includes_the_medulla_oblongata%2C_the_pons_and_the_midbrain_%282%29_CRUK_294.svg
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e0/Blausen_0114_BrainstemAnatomy.png
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/af/1202_White_and_Gray_Matter.jpg/512px-1202_White_and_Gray_Matter.jpg