PDF chapter test TRY NOW
Magnetic Separation Method:
Principle:
Magnetic separation is based on the principle of magnetic properties of the components of the ore. If either the ore particles or the gangue can be attracted in a magnetic field, magnetic separation can be used.
Example:
Tinstone \(SnO_2\), the ore of tin.
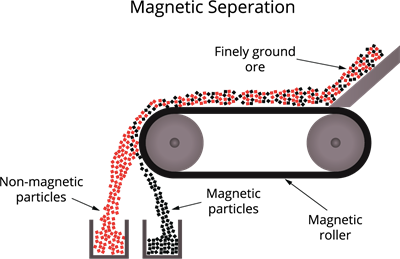
Separation of substance using magnets
Method:
- The crushed ore is discharged into a conveyer belt that revolves around two metal wheels, one of which is magnetic.
- Magnetic particles are drawn to the magnetic wheel and separated from non-magnetic particles.

Ore discharging conveyor
(iii). Froth Floatation:
Principle:
Froth floatation method is based on the principle that the metallic sulphide particles of ore are preferentially wetted by oil (pine oil) and the gangue particles by water.
Lighter ores, such as sulphide ores, are concentrated by this method.
Example:
Zinc blende (\(ZnS\)).
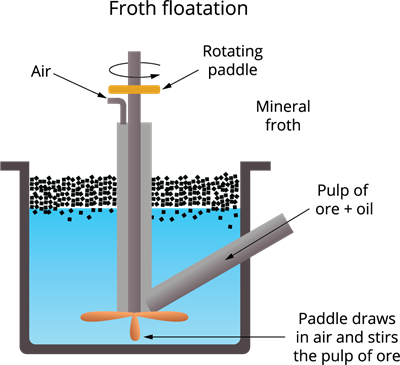
Froth floatation
Important!
Note: This method is used when the impurity is heavier than the ore.
Method:

Ore and oil mixing tank
- The crushed ore is stored in a large tank containing pine oil and water and agitated with a compressed air current.
- The oil wets the ore, which separates it from the gangue as froth. Because the ore is lighter, it floats to the surface with the froth, leaving the impurities behind.
