PDF chapter test TRY NOW
Epithelial cells:
- These are the cells that form the surfaces of body, such as the skin, blood vessels, urinary tract and organs.
- These cells are mostly flat and columnar in shape.
- The major function of these cells is to cover the surface of the body for protection.
- Hence these cells are known as the safety shields of the body.
- The epithelial cells are the first cells that come into contact with external stimuli, such as chemicals and particulate materials.
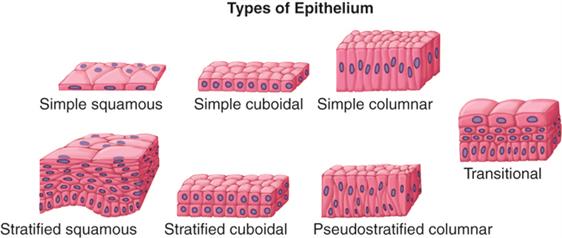
Types of epithelial cells
Muscle cells:
- These cells are commonly known as myocytes.
- The muscle cells are the cells that make up the muscle tissue.
- They are long and spindle-shaped cells.
- These cells can contract and relax, allowing the cell movement.
- The \(3\) types of muscle tissues are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal tissues.
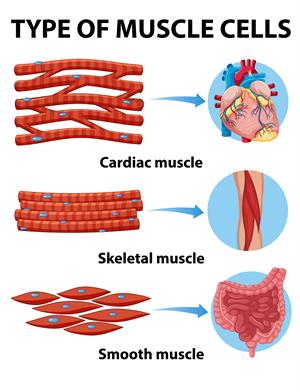
Types of muscle cells
Nerve cells:
- The nerve cells are electrically excitable.
- These cells have the ability to communicate with the other cells.
- The body of the nerve cells is branched with an elongated nerve fibre.
- These cells are specialised to carry and conduct messages that coordinate the functions of the body.
- It is the main component of nervous tissues in all animals.
- It is absent in plants and fungi.
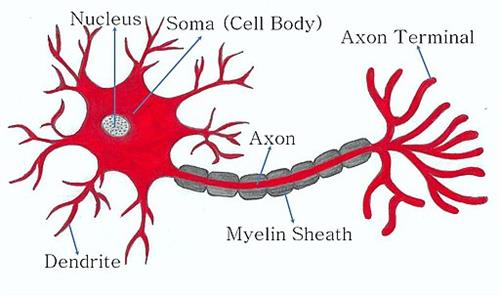
Structure of neuron
Red blood cells or erythrocytes:
- These are the cellular components of blood that transport the oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
- They are also known as erythrocytes.
- They are round, biconcave and disc-shaped.
- They also collect carbon dioxide from the various parts of the body.
- The red blood cells contain a special protein called haemoglobin, which helps carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and then returns carbon dioxide from the body to the lungs so it can be exhaled.
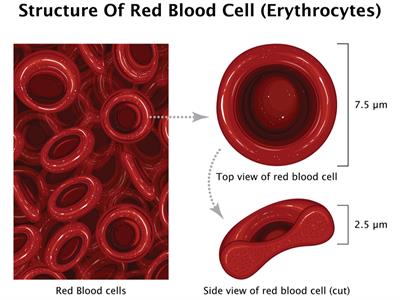
Red blood cells
Reference:
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/cuny-csi-ap-1/chapter/integumentary-levels-of-organization/
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Neuron_typical_structure.jpg/512px-Neuron_typical_structure.jpg
https://www.vecteezy.com/vector-art/1424590-type-of-muscle-cells-chart
