
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoRed data book is a file or sourcebook for recording rare and endangered species - animals, plants and fungi.
Local sub-species present within the territory of a state or country are recorded in the red data book. It gives important data for observational studies and monitoring programmes on habits and habitats of rare and endangered species.
It is created to identify and protect species that are about to be extinct. It is maintained internationally through the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). It is an international organization that works in nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
IUCN was founded in \(1964\) to maintain a complete record of all species that lived. The book classifies species into \(three\) categories - threatened, not threatened, and unknown. Book has the information why the species has become extinct, along with population trends and distribution.
Red data book contains colour-coded information sheets like black for species that are extinct, red for endangered species etc. In the book, they are arranged according to the extinction risk of species and subspecies.
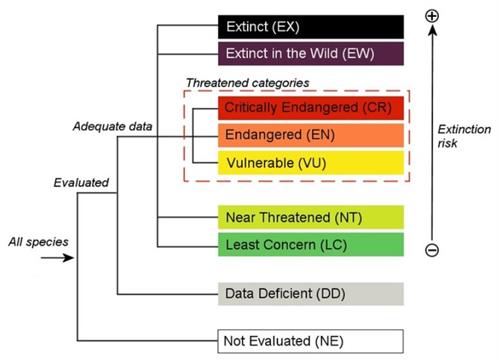
Advantages of Red data book:
1. Helps to evaluate the population of particular species.
2. Data available in the book is used to evaluate the species at the global level.
3. It helps to identify all the animals, birds and other species about the conservation status.
4. With the help of the book, risk of a species that becomes globally extinct can be estimated.
5. The book provides a framework or guidelines for implementing protective measures for species that are endangered.
Disadvantages of Red data book:
1. Information available in the book is incomplete. Many species, both extinct and endangered are not updated in this book.
2. Source of the book's data has been hypothesized or speculated.
3. The book maintains a complete record of all animals, plants and other species but does not have information on the microorganisms.
Red Data Book of India:
India is a highly diverse country with only \(2.4 \ %\) of the world’s land area. It accounts for \(7 - 8 \ %\) of all recorded species, that includes over \(45,000\) species of plants and \(91,000\) species of animals.
India has diverse physical features and climatic conditions that resulted in various ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, deserts, coastal and marine ecosystems that harbour and sustain high biodiversity and contribute to human well-being.
Example:
Some of the endangered animal species present in the Red data book of India include flying squirrels, blackbucks, Indian giant squirrels, snow leopards, one-horned rhinoceros, Himalayan musk deer etc.
Four out of \(34\) globally identified biodiversity hotspots, the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, the North-East, and the Nicobar Islands, can be found in India. India became a State Member of IUCN in \(1969\), through the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
The IUCN India country office was established in \(2007\) in New Delhi. Red Data Book of India
contains the conservation status of animals and plants found in the Indian subcontinent. The data for the book is provided through surveys which are conducted by the Zoological Survey of India and the Botanical Survey of India under MoEFCC.
contains the conservation status of animals and plants found in the Indian subcontinent. The data for the book is provided through surveys which are conducted by the Zoological Survey of India and the Botanical Survey of India under MoEFCC.
Reference:
http://www.whalesharkdiaries.com/awareness-education/international-whale-shark-day-august-30-2017/