
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoThe Consumer Protection Act, \(1986\) (COPRA)
To protect the interests of consumers, the Parliament of India enacted the Consumer Protection Act, \(1986\). This act came into force on December \(24\), \(1986\).
For checking unfair trade practices, 'defects in goods' and 'deficiencies in services' in India, COPRA is regarded as the 'Magna Carta' in the field of consumer protection. COPRA led to the establishment of a widespread network of consumer forums and appellate courts all over India.
To increase consumer awareness, Consumer Protection Councils are established at the national, state and district level.
Consumer Disputes Redressal Agencies
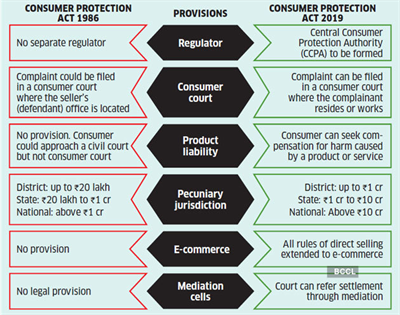
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC): By Central government, deals cases with more than \(10\)million (Above \(Rs.\) \(1\)Crore).
- State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (SCDRC): By state government. Also known as State commission, takes up cases between \(Rs.\)\(20\)Lakh and Up to \(Rs.\)\(1\)Crore.
- District Consumer Disputes Redressal Forum (DCDRF) (District forum): Established in each district by the state government, deals with cases Up to \(Rs.20\)lakh.
Consumer Protection Act of \(2019\)
In August \(2019\), the Indian Parliament passed the Consumer Protection Bill, (\(2019)\), which aims to solve consumer disputes in this Digital Age. This act came to force on July \(20\), \(2020\).
Important provisions of the New Act:
- E-Commerce Transactions: The act has enhanced the meaning of consumer, any person who buys any goods, whether, through offline or online transactions, electronic means or teleshopping is now included under the definition of customer.
- Enhancement of Pecuniary Jurisdiction: Revised pecuniary limits have been fixed under the New Act.
- District forum - Up to \(Rs.\) \(1\)Crore
- State commission: Between \(Rs.\) \(1\)Crore and up to \(Rs.\)\(10\) Crore
- National commission: Above \(Rs.\)\(10\)Crore
Customers can now file complaints electronically by this new act. - Central Consumer Protection Authority: An regulating authority known as Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) will be established, and it will have an investigation wing, and that will be headed by Director- General to investigate consumer law violations. It will be headquartered in New Delhi.
- Unfair Trade Practices now include sharing of personal information given by the consumer in confidence, unless such disclosure is made in accordance with the provisions of any other law.
- Penalties for Misleading Advertisement:
CCPA may impose a \(10\)lakh or imprisonment for up to two years on a manufacturer or an endorser, for a false or misleading advertisement. If the offence is repeated again, then fine of \(Rs.\)\(50\)lakh and imprisonment of up to five years can be imposed.
Consumer courts in India:
National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC): It is Apex body of Consumer Courts in India. It is a quasi-judicial commission in India which was set up in \(1988\) under the Consumer Protection Act of \(1986\). The commission is headed by a sitting or retired judge of the Supreme Court of India. Its head office is in New Delhi.
State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (SCDRC): State Commission has the appellate jurisdiction over the District Forum.
District Consumer Disputes Redressal Forum (DCDRF): Works at the district level.
Important acts in India:
- The Consumer Protection Act, \(1986\)
- The Legal Metrology Act, \(2009\)
- The Bureau of Indian Standards Act, \(1986\)
- The Essential Commodities Act, \(1955\)
- The prevention of Black Marketing and maintenance of supplies of essential Commodities Act, \(1980\)
For more understanding visit the below websites.
Website of the Department: Consumer Affairs
Website of the NDRC : NDRC
State commission : State commission
District forum : District forum