
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoThe Mughal rule:
The Mughal empire was famous and kept as a benchmark in the field of administration which they adopted from their ancestors. They exhibited a proper structure in administration which was split into three layers.
- Central Administration.
- Provincial Administration.
- Local Administration.
Central Administration of Mughals:
- The Emperor was the central authority in Mughal administration where he holds the supreme power over the law making and Final arbitrator of Justice. He also appointed separate officers to look after the affairs of the departments allocated to them.
- The Mughal administration under the emperor had four main divisions.
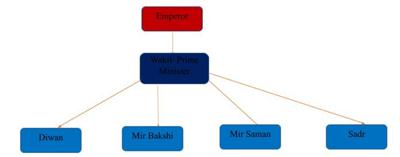
- Wakil: He is the Prime Minister of the main provinces of the Mughal empire who overlooked the administration of other departments. He was under the direct control of the Emperor.
- Diwan: He is the Chief Minister who worked under the Wakil and the controller of revenue and finance of all the departments functioning in the empire.
- He also assigned the duties and revenue for Faujdars of the Province.

Mughal Emperor in his court
- Mir Bakshi: He was the head of Military affairs under the Mughal administration who looked over the recruitment of soldiers, entering their role in the Mansabdari system, and maintaining their ranks.
- Mir Saman: Also known as the Khan-i-Samman look after the royal household. He maintained the records of “Kharkhanas or royal workshops”.
- Sadr: He was the head of religious departments, collected charity and other revenue to enhance education in Madrasas.
The Mughal Provincial Administration:
The Mughal emperors divided their provinces named “Subas” which was headed by “Subedars”. The Suba’s are further divided into three groups.
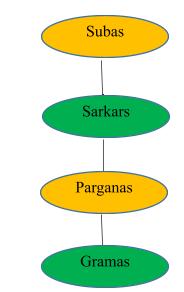
The Subas are further divided into Sakars or districts, and when the group of villages are combined they are called Parganas. Villages or Grama are the lowest unit of administration under Mughals.
Local Administration: