
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free Demo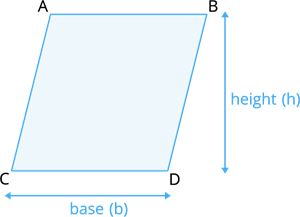
Area:
To calculate the area of a parallelogram, we multiply the base(\(b\)) times the height(\(h\)).
Area of parallelogram \(A = b × h\) square units.
For example, A parallelogram has a base of \(6 m\) and height of \(3 m\). Find its Area?
base \((b)=6\ m\) and height \((h) = 3\ m\).
Area
Base:
To calculate the base of the parallelogram, we divide area \(A\) by height \(h\).
Base of parallelogram (\(b\)) \(= A/h\) unit.
For example, A parallelogram has an area of \(64 m²\), and is \(4 m\) height, what is its base?
Area \((A)=64\ m^2\) and height \((h)=4\ m\).
Base
Height:
To calculate the height of the parallelogram, we divide the area \(A\) by base \(b\).
Height of parallelogram (\(h\)) \(= A/b\) unit.
For example, A parallelogram has an area of \(64 m²\) and base is \(16 m\). Find its height?
Area \((A)=64\ m^2\) and base \((b)=16\ m\)
Height
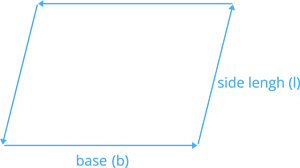
Perimeter:
To calculate the perimeter of a parallelogram, we multiply \(2\) times the (base + side length).
Perimeter of parallelogram (\(P\)) \(= 2 (b + l)\).
Where \(b\) is denoted as base and \(l\) is denoted as side length.
For example, A parallelogram has a base of \(5 m\) and length of \(3 m\). Find its perimeter?
Base \((b)=5\ m\) and side length \((l)=3\ m\).
Perimeter