PDF chapter test TRY NOW
During radioactivity, the radioactive nucleus emits harmful radiation. These radiations consist of three types of particles. They are
- Alpha (\(α\)) rays
- Beta (\(β\)) rays
- Gamma (\(γ\)) rays
Some amount of radioactive material was kept inside a block of lead. A positively charged plate was placed on the right side and the negatively charged plate on the left side of the lead block. Then, the harmful radiations emitted from the radioactive material were allowed to pass through an electric field.

Deflection of particles in an electric field
The constituents that are deflected towards the negative plate are known as Alpha rays (α- rays).
The constituents that got deflected towards the positive plate was called Beta rays (β- rays).
The constituents that are not deflected are called Gamma rays (γ- rays).
The constituents that got deflected towards the positive plate was called Beta rays (β- rays).
The constituents that are not deflected are called Gamma rays (γ- rays).
Alpha rays:
Alpha rays are the helium nucleus (\(_{2}He^{4}\)) consisting of two protons and two neutrons. They are positively charged particles, having a charge of \(+2e\).

Ejection of alpha particle
Properties of alpha particles:
1. The ionising power of alpha particles is \(100\) times greater than \(β\ rays\) and \(10,000\) times greater than \(γ\ rays\).
2. They have low penetrating power such that they can even be stopped by thick paper.
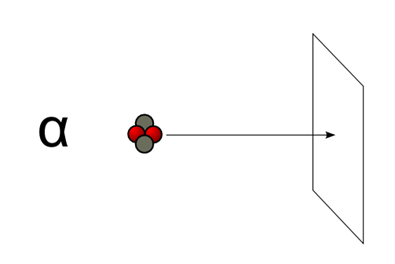
Alpha particle hitting a paper
3. According to Fleming’s left-hand rule, the \(α\ rays\) are deflected by the electric and magnetic fields.
4. The speed of alpha rays ranges from \(1/10\) to \(1/20\) times the speed of light.
To study about Fleming’s left-hand rule, click here.
Reference:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/52/Alfa_beta_gamma_neutron_radiation_M1.PNG
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/21/Alpha-decay-example.svg
