
PUMPA - SMART LEARNING
எங்கள் ஆசிரியர்களுடன் 1-ஆன்-1 ஆலோசனை நேரத்தைப் பெறுங்கள். டாப்பர் ஆவதற்கு நாங்கள் பயிற்சி அளிப்போம்
Book Free DemoWe know the difference between an atom, an element and a compound. Let us now learn about the term called 'atomicity'.
In chemistry, atomicity refers to the total number of atoms present in a single molecule of an element, compound, or substance. The number of atoms present in a single molecule is termed its atomicity.
We can distinguish the molecules respective to the number of elements they combined to form a molecule.
Let's look at how to figure out while calculating the atomicity of elements and compounds:
Let's look at how to figure out while calculating the atomicity of elements and compounds:
Example:
1. 

\(O + O \rightarrow O_2\)
Here, \(O\) refers to Oxygen atom.
Therefore, to calculate the atomicity, simply add the number of atoms together \(1 + 1 \ = 2\)
Oxygen is a diatomic molecule, meaning that each molecule contains two atoms, giving it an atomicity of two.
2. 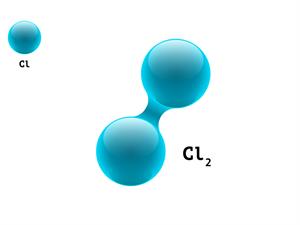

\(Cl + Cl \rightarrow Cl_2\)
Here, \(Cl\) refers to Chlorine atom.
\(1 + 1 \ = 2\)
Chlorine is a diatomic molecule. It means that each molecule contains two atoms, giving it an atomicity of two.
3. 

\(Na\)
Here, \(Na\) refers to sodium atom.
\(1\) atom.
Sodium is a monoatomic element. It means that each molecule contains one atom, giving it atomicity of one.
For a molecule with multiple elements,
1. 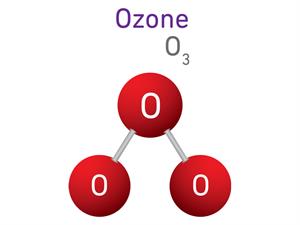

\(O_2 + O \rightarrow O_3\)
Here, \(O\) refers to Oxygen atom, and \(O_2\) refers to oxygen molecule.
\(2 + 1 \ = 3\)
Ozone is a triatomic molecule, meaning that each molecule contains three atoms, giving it an atomicity of three.
2. 

\(C + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2\)
Here, \(C\) refers to Carbon atom, and \(O_2\) refers to oxygen molecule.
\(1 + 2 \ = 3\)
Carbon dioxide is a triatomic compound, meaning that each molecule contains three atoms, giving it an atomicity of three.
3. 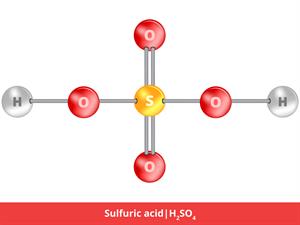

\(H_2SO_4\)
Here, \(H_2\) refers to hydrogen, and \(O_4\) refers to oxygen, and \(S\) refers to sulphur.
\(2 + 1 + 4 \ = 7\)
Sulphuric acid is a compound, giving it an atomicity of seven.
4. 

\(H_2O\)
Here, \(H_2\) refers to hydrogen, and \(O\) refers to oxygen.
\(2 + 1 \ = 3\)
Water is a compound, giving it an atomicity of three.
5. 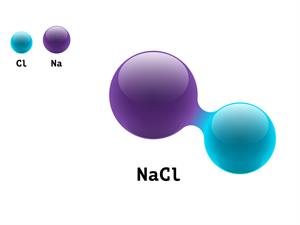

\(NaCl\)
Here, \(Na\) refers to sodium atom, and \(Cl\) refers to chlorine atom.
\(1 + 1 \ = 2\)
Sodium Chloride is a compound, giving it an atomicity of two.
Few more examples for elements and their atomicity.
Classification of elements | Name of the elements | Symbol | Atomicity |
Metals | Aluminum | \(Al\) | \(1\) |
Copper | \(Cu\) | \(1\) | |
Iron | \(Fe\) | \(1\) | |
Non-metals | Helium | \(He\) | \(1\) |
Hydrogen | \(H_2\) | \(2\) | |
Nitrogen | \(N_2\) | \(2\) | |
Fluorine | \(F_2\) | \(2\) | |
Phosphorous | \(P_4\) | \(4\) |
Reference: