UPSKILL MATH PLUS
Learn Mathematics through our AI based learning portal with the support of our Academic Experts!
Learn moreTime is specified in two ways.
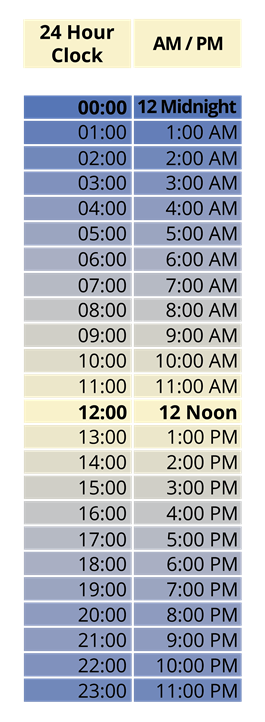
1. Ordinary time or \(12\)-Hour format
2. Railway time or \(24\)-Hour format
Ordinary Time or the 12-Hour Format:
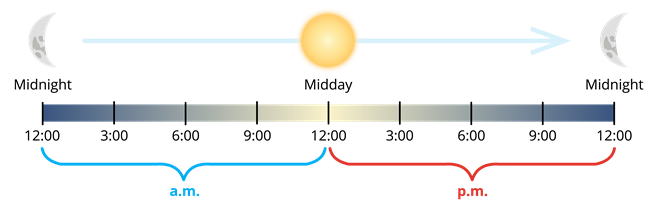
- A day has \(24\) hours. It is divided into two periods; each has \(12\) hours.
- \(12\!:\!00\) at night is called midnight, and \(12\!:\!00\) at day is called noon.
- The \(12\) hour clock has Ante Meridien (a.m.) and Post Meridien (p.m.).
- Ante Meridien \(-\) Midnight \(12\!:\!00\) to Noon \(12\!:\!00\)
- Post Meridien \(-\) Noon \(12\!:\!00\) to Midnight \(12\!:\!00\)
Example:
1. \(9\!:\!00\) a.m. means \(9\)'O clock in the morning (before noon).
2. \(9\!:\!00\) p.m. means \(9\)'O clock in the night (after noon).
Railway time or \(24\)-Hour format:
- \(24\)-hour clock mostly followed in railways, airways and defence.
- It is the clock from \(0\) hours to \(24\) hours.
- \(24\)-hour time format usually has \(4\) digits. First, two digits are hours, and the last two digits are minutes.
- We don't need to mention morning, noon, evening and night in the \(24\)-hour clock.
- \(12\) at midnight is denoted as \(00\!:\!00\) hours.
Example:
1. \(2\!:\!00\) in the after noon \(=\) \(14\!:\!00\) hours
2. \(6\!:\!00\) in the evening \(=\) \(18\!:\!00\) hours
\(12\)-Hour format and \(24\)-Hour format: